Abstract
The clinical significance of minimal residual disease (MRD) in patients with relapsed/refractory hairy cell leukemia (r/r HCL) who have achieved complete response (CR) has not been demonstrated. In other hematologic malignancies, MRD eradication may be associated with prolonged clinical response (Hourigan et al. Leukemia 2017;31:1482-90; Lahuerta et al. J Clin Oncol 2017;epub ahead of print). Moxetumomab pasudotox (formerly CAT-8015), a recombinant immunotoxin fusion protein that specifically binds to B lymphocyte-specific surface antigen CD22, has been shown by flow cytometry to eradicate MRD in a significant (P= 0.04) percentage of patients with r/r HCL (Kreitman et al. ASCO 2015). However, a detailed study of MRD by bone marrow immunohistochemistry (IHC) was not previously presented. We analyzed data from a phase 1 dose escalation study of moxetumomab pasudotox in r/r HCL patients to test the hypothesis that eradication of MRD in bone marrow, assessed by IHC, may be associated with prolonged remission.
CAT-8015-1001 (NCT00586924) was a phase 1 study evaluating the safety and efficacy of moxetumomab pasudotox in patients with r/r HCL who previously had received at least 2 courses of treatment, at least 1 of which included a purine analog; initial results from the dose escalation phase in 28 patients have been reported (Kreitman et al. J Clin Oncol 2012;30:1822-8). Moxetumomab pasudotox was administered on days 1, 3, and 5 of each 28-day cycle until 2 cycles past complete remission (CR), disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or neutralizing antibodies. In the dose escalation phase, 28 patients received moxetumomab pasudotox 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, or 50 µg/kg. An additional 21 patients were enrolled in the 50-µg/kg cohort.
Bone marrow samples were obtained at baseline and at multiple time points during and after treatment. A central pathology laboratory performed hematoxylin and eosin and IHC staining for HCL/B-cell antigens CD20, CD79a, Annexin A1, DBA.44, and PAX-5. A blinded independent central pathologist reviewed (BICR) and assessed stained slides as IHC MRD+ or IHC MRD− for each time point.
The best BICR IHC MRD response was compared with the best investigator-reported (IR) disease response. Duration of CR, duration of response (DOR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival were evaluated for patients with a best response of BICR IHC MRD+ vs MRD−.
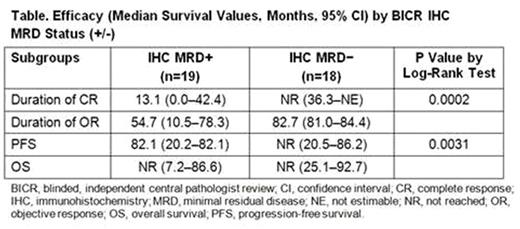
Thirty-seven patients were evaluated for BICR IHC MRD; posttreatment bone marrow biopsies were not available for 11 patients, and biopsies from one patient were non-evaluable. The BICR IHC MRD status appears to be associated with the IR response; 17 of 18 BICR IHC MRD− patients had a best response of CR vs 9 of 19 MRD+ patients. Among patients found to be BICR IHC MRD− at 1 or more posttreatment evaluations, median duration of CR and median PFS were not reached after 84 months of follow-up vs 13.08 and 82.07 months, respectively, for patients who were consistently MRD+ at all time points. DOR was 82.7 vs 54.7 months for the BICR IHC MRD− and MRD+ groups, respectively.
Cladribine monotherapy and cladribine followed by rituximab eliminated IHC MRD in some newly diagnosed HCL patients (Sigal et. al, Blood 2010;115:1893-6; Ravandi et. al Blood 2011;118:3818-23). Although vemurafenib demonstrated 96% to 100% overall response rates and 35% to 42% CR rates in patients with r/r HCL, all CR patients were IHC MRD+, and duration of MRD+ CRs was 19 months (Tiacci et al. N Engl J Med 2015;373:1733-47). Moxetumomab pasudotox is, to our knowledge, the only non-chemotherapy regimen shown to eradicate MRD in a meaningful percentage of patients with r/r HCL. Here, BICR findings confirmed elimination of IHC MRD in 49% of evaluable patients. MRD− patients experienced a statistically significantly longer duration of CR (P=0.0002) and PFS (P=0.0031) vs MRD+ patients.
Based on the results of this retrospective analysis, together with observations made in the vemurafenib study, BICR IHC MRD− vs MRD+ status is associated with extended DOR and PFS in patients with r/r HCL treated with moxetumomab pasudotox. If this finding can be replicated in additional clinical studies, including the phase 3 pivotal study of moxetumomab pasudotox, IHC MRD determinations may be useful in evaluating the efficacy of therapies in the r/r HCL population.
Kreitman: NIH: Patents & Royalties: Co-inventor on pending Moxetumomab Pasudotox patent owned by NIH. Robak: Akari Therapeutics Plc: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding. Coutre: Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding. Marshall: MedImmune: Employment. Yang: MedImmune: Employment, Equity Ownership, Other: Travel expenses. Pastan: NIH: Patents & Royalties: Pastan is an inventor on several patents on immunotoxins that have all been assigned to the NIH. Yao: MedImmune: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal